
Using volumetric capnography, the VD phys is divided into three dead space components: airway dead space (VD aw), alveolar dead space (VD alv), and shunt dead space (VD shunt). PC-IRV or pressure-controlled ventilation with sufficient inspiratory time might reduce the VD phys.

VD phys represents the overall ventilatory efficiency, including circulatory dynamics, and a total of ventilation/perfusion ( ) mismatch. However, serum cytokine levels are affected not only by the ventilator setting, but also by duration, surgical invasion, bleeding, and any stress to the patient. However, another randomized controlled study reported no differences between the lung-protective properties of PC-IRV and volume-control ventilation (VCV) when performed for >2 h in robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy, as determined by the changes in serum cytokine levels.
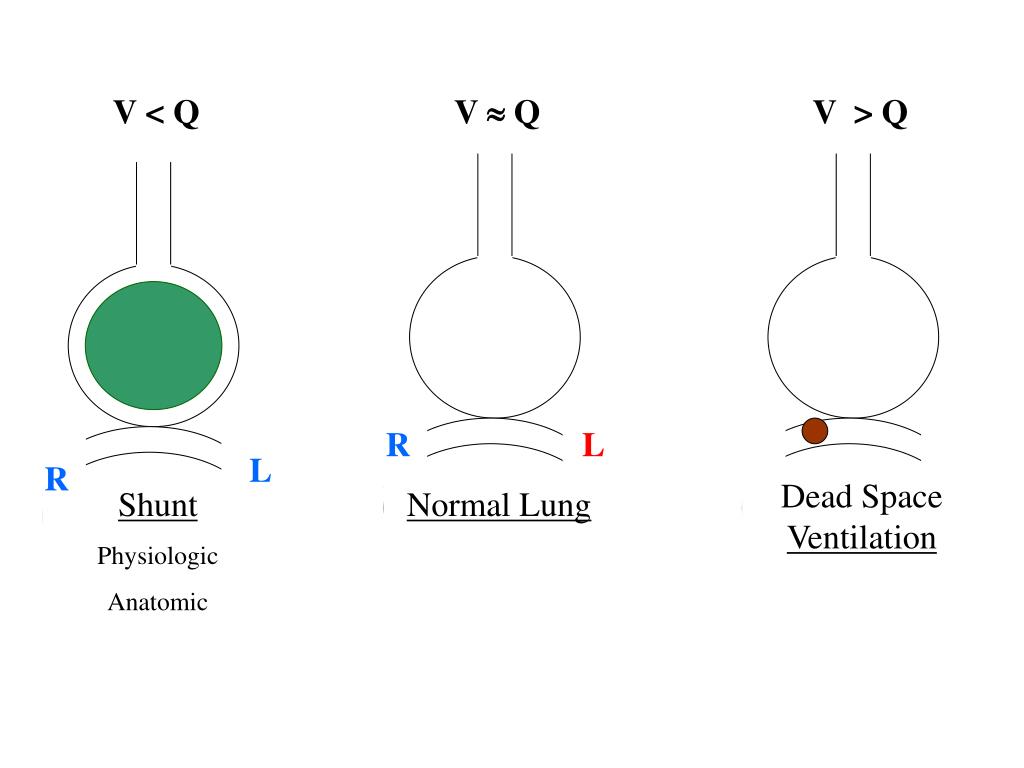
We believe that PC-IRV might be a lung-protective ventilation strategy. Previously, we studied the changes in dead space components within a short duration (30 min) of each ventilator mode using a cross-over study design, and reported that pressure-controlled inverse ratio ventilation (PC-IRV) reduces the physiological dead space (VD phys).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
